The key to managing the impacts of climate change is resilience. Resilience is the ability of a system or organization to adapt to dangerous events. It often centers on the resilience of buildings stock. These efforts are meant to reduce the risks associated with buildings and supply chains. These efforts are generally carried out through policy and decision makers. It is difficult to achieve resilience. This article will discuss how resilience is defined and implemented in the construction sector. It will also explain how it can be measured. Stakeholders can use resilience information to identify potential adaptation opportunities and make informed decisions.
Many academic disciplines have studied climate change resilience. For instance, there has been a strong focus on resilience in cities. Specific hazards, like flooding or seismic activity, can be improved by strategies. Additionally, these strategies seek to reinforce emergency responses, and reduce the recovery time frame.

Studies in the ecological domain define resilience as the ability of a system to retain essential processes and structures. A resilient built environment is one that can withstand extreme natural hazards such as hurricanes and floods. It can also reduce human-caused dangers like wildfires. Although this definition is simplistic, it accurately reflects current knowledge about resilience.
Social science resilience is another area of emphasis. This domain addresses the interplay among system components, such communities, and identifies important roles for government and business. One strategy to improve resilience is strengthening social cohesion, and community empowerment. This strategy, although not well-known, does indicate the need to make adaptation efforts.
Other resilience strategies involve the development of alternative interventions, such as solar panel kits. These may be more cost-effective than rebuilding, especially in low-resource settings. However, these techniques come with limitations. They might not be possible in remote areas or hard to reach places.
Diverse efforts to improve climate resilience are also characteristic of their success. The Northern Institute of Applied Climate Science for example has incorporated traditional ecological wisdom into its research. There are also various international coalitions dedicated to resilience, such as the Adaptation Research Alliance. All of these initiatives share best practices, provide metrics and mobilize the countries.
Finance is another area of interest. Through the Executive Order on Tackling Climate Crisis, the United States is trying to increase resilience finance. This includes coordination among different departments and agencies. Similarly, the United Kingdom has put additional emphasis on adaptation at the G7 Summit in 2021.
Finally, there is a robust literature on resilience in the social sciences, which addresses factors affecting climate change responses. Some studies have investigated resilience theoretical frameworks. Others have investigated the effects of resilience and economic well-being. While the majority have focused on disaster-risk reduction, other resilience strategies are being explored in social science.
As strategies and resilience approaches develop, it is important that professionals understand the implications of different definitions. Understanding the various definitions can help stakeholders choose the most appropriate approach for the particular setting.
FAQ
What are the causes of climate change?
Climate change, which is a global phenomenon, has been driven by an increased amount of greenhouse gases from human activity. The increase was primarily caused by fossil fuel burning to generate electricity and transport. These emissions lead to a greater amount of sun's energy being trapped in Earth’s atmosphere, which results in rising temperatures.
Climate change is also caused in part by human population growth, the destruction and clearing of ecosystems, energy consumption and overgrazing. This decreases the amount naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Climate change can also come from natural forces, such as changes in solar energy.
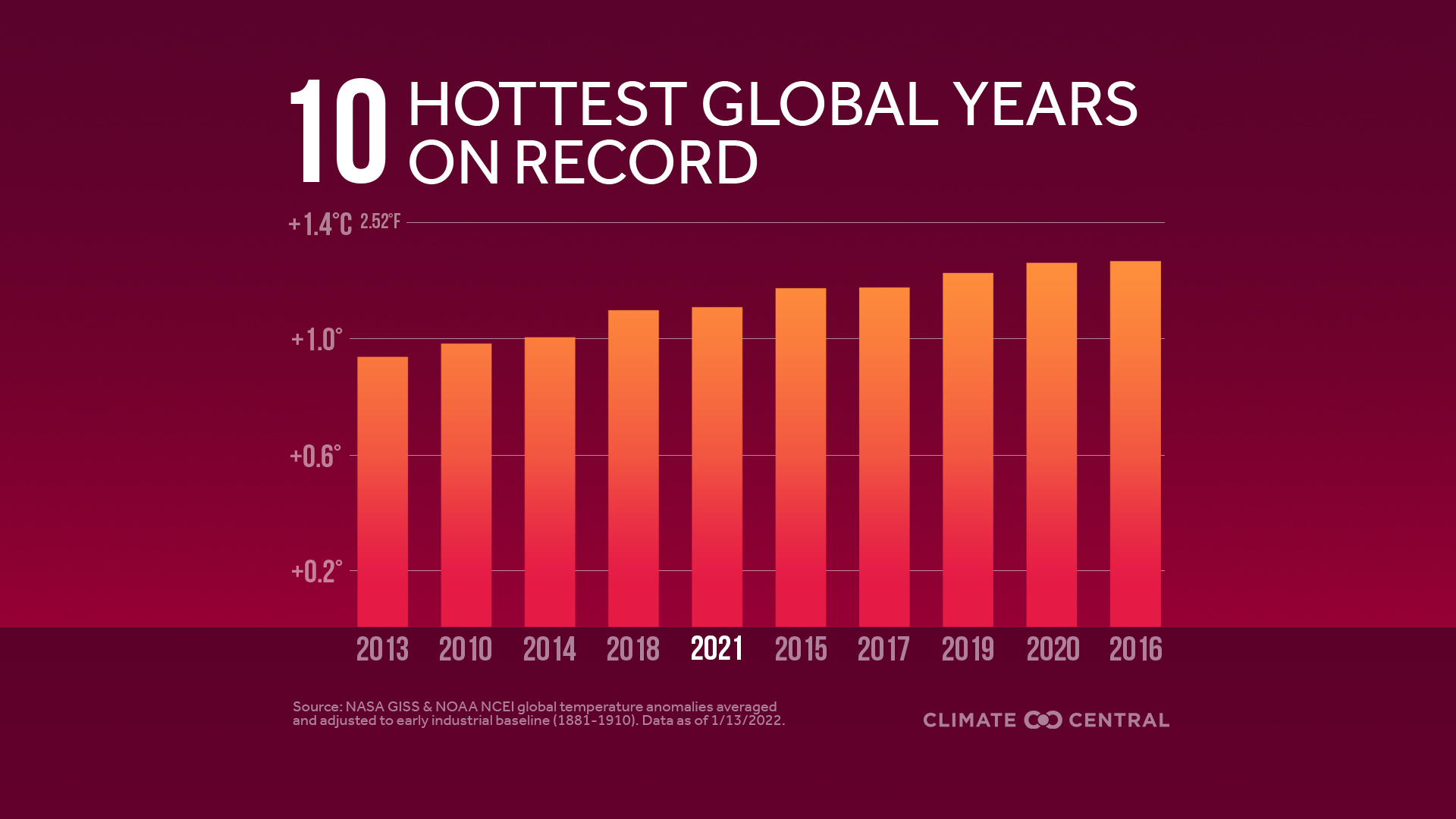
These combined human activities result in overloading Earth's capacity to properly balance its energy budget, leading to an average increase of 1 degree Celsius globally since pre-industrial times. As the oceans absorb most heat energy, glaciers melt more quickly than they form. Other adverse consequences include water shortages and droughts as well as extreme weather events, such as flooding and hurricanes, which are often caused by heavy rains on soils.
It is vital that we reduce our carbon footprint immediately and stop releasing greenhouse gases. This will help us protect ourselves against further damage from climate change. Along with reducing our dependence upon fossil fuels to generate electricity, it is important to invest in renewable sources like wind turbines or solar cells that do not emit harmful pollutants into nature. Also, reforestation is a sustainable practice that can restore balance to the delicate planetary cycles which are essential for our survival.
What is the effect of climate change upon biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change is having a wide range of effects on biodiversity as well as ecosystems. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
These changes can result in shifts of habitat areas, disrupting food chains or affecting population numbers or distributions. With potentially devastating consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems and their functioning, these shifts in climate conditions could cause significant impacts. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Moreover, changes to climate result in rising temperatures and more frequent extremes such as droughts and floods which puts more stress on already fragile systems such as coral reefs or tropical rainforests. It is estimated that up to 30% of animal species could become extinct due to climate change by 2050, which would spark a cascade of further losses within ecological communities.
Climate change poses a significant threat to biodiversity and human societies, as well as to ecosystems that provide food, water, timber, or other services. You can mitigate the effects of climate change at all levels by reducing global warming trends. Further, future damages can be prevented with good management practices.
What is the potential of new technologies to combat climate changes?
There are many technologies that can be used to tackle this global problem. Advances in applied science make it possible to move to a more sustainable future.
For lowering greenhouse gas levels, there are new carbon capture and sequestration methods. In addition to reducing emissions from livestock and soil degrading, enhanced agricultural practices can help reduce them. Smart grid technology may also be used to boost efficiency and improve building design.
The latest synthetic biology methods allow scientists to create organisms that can use green sources of fuel like the CO2 laser as biofuels or alternative feedstocks. This could be a major shift in transportation if there is a shift away from petrol-based vehicles to electric cars powered solely by renewable sources.
Finally, increased investment in digital technology can empower people across borders with more access to data about their ecological footprints and allow them to make better decisions regarding their consumption habits. Understanding how we contribute to the carbon production of our planet is key for better stewardship.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to include sustainable practices in your daily life to combat climate changes
Reducing your consumption of energy and food is one way you can integrate sustainable practices into your day. Shopping secondhand and borrowing items from family and friends is a better option than buying new products every day. In order to reduce the amount methane in the atmosphere, it is a good idea to eat vegetarian meals only once or twice per week. Finally, whenever possible, turn off the lights when leaving a room to conserve energy.
Another way to fight climate change is by decreasing emissions from transportation sources like cars and airplanes through carpooling or taking public transit instead of driving alone. In place of traditional fossil fuels, we can choose to use renewable power sources such solar panels to generate electricity at our homes. In order to take effective action against climate change, it is vital that policy makers support clean air regulations. Also, engaging with other citizens on issues such plastic pollution reduction and deforestation will help to create more conscious citizens that will take action.