
The Paris agreement is a global agreement that aims to reduce greenhouse gas emission. It is an international convention based on Intended Nationally Determined Contributions. For the Paris Treaty to work, all countries must agree to set goals and targets. Several courts have already recognized the Paris treaty as a legally binding agreement. The treaty's legal significance is not lost on the United States, but it has not been formally withdrawn from.
The United States participates actively in United Nations meetings. The United States has signed the Paris Agreement as part of this process. But, President Donald Trump announced his intention to withdraw the United States from the deal in June. Unlike other nations, the United States cannot formally withdraw from the treaty until 2020.
According to US Department of State, Paris treaty is a Treaty because it can be implemented through state laws without congressional approval. It's not easy to implement the treaty. This is due to the lack of an overarching body, sanctions, and a central authority. The Paris Treaty's agenda is driven primarily by the rich nations. These nations are responsible for most of the global pollution, and have the most incentive to continue the fight against climate change.
At the moment, seven out ten Americans don't want the United States staying in the treaty. Nevertheless, the Paris treaty has been seen as a major turning point in the history of climate litigation. Several landmark cases have been won by environmental groups against governments.
There was much discussion about the effectiveness of the Paris Treaty during its creation. The treaty was crafted by delegate after long and difficult work. The treaty was designed to be balanced between science and business and to encourage international cooperation in fighting climate change. The treaty has two main goals: to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions and to improve international response.
The United States and other countries developed expressed their willingness to limit global warming to below 2 degrees Celsius in the course of the negotiations. Despite their pledges, there was some disagreement between the United States' contributions and those of other countries. China and Saudi Arabia were two of the main objections. Although the United States has not withdrawn from the UNFCCC, it has rolled back the Clean Power Plan. Scientists also don't consider the Paris Agreement’s target to keep temperatures below 2 degrees Celsius strong enough.
At the COP21 meeting in Paris, several countries argued against the target. Further, the targets were established separately for each country. While this was a step up from the Kyoto Protocol's SED, it was not accepted by all countries. The treaty contains a clause that allows members to revise their pledges for 2018.
Similarly, the Environmental Protection Agency rolled back the Clean Power Plan. Joe Biden, President-elect, pledged to rejoin the Paris Agreement on January 20, 2021. The depositary was also notified.
FAQ
What is climate change and how does it occur?
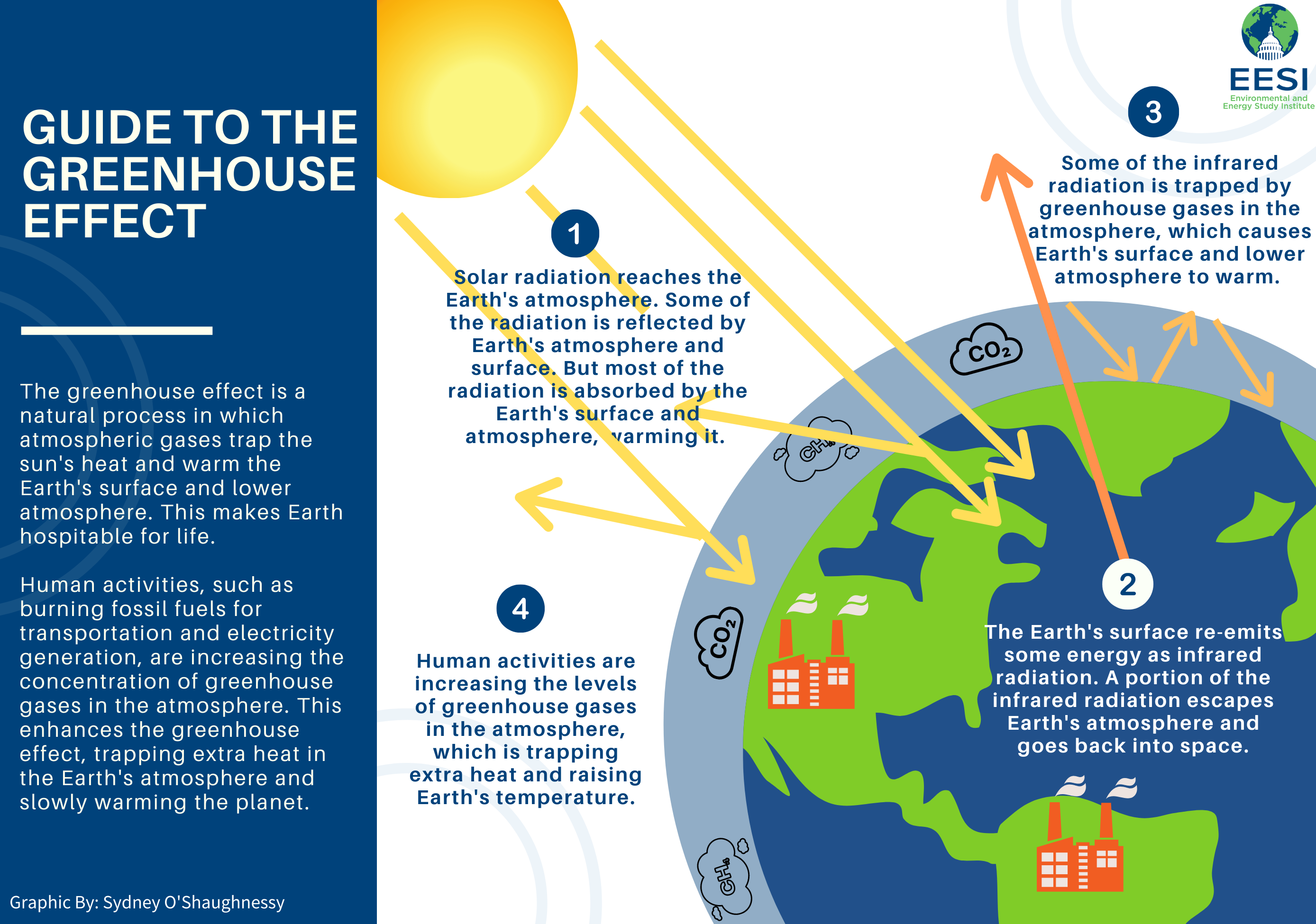
Climate change is the long-term shift in global weather patterns caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat which causes global temperatures to rise. This can cause a wide range of changes in weather conditions and climate. These can include rising sea level, melting glaciers or droughts, widespread coral bleaching, species extinction and disruptions in food production.
The main cause of climate change is human activity such as burning fossil fuels for electricity and transportation, cutting down forests, and farming livestock. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
The deforestation plays an important role in contributing approximately 15-20% to global greenhouse gas emissions. When trees are cut down or burned it releases their stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Forests are also a natural carbon-sink that removes carbon dioxide from the air. Without this absorption capacity, carbon levels will continue increasing with devastating consequences for the ecosystems around the globe.
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). While methane is used extensively in industrial processes, it contributes substantially to atmospheric heating. N2O comes primarily from soil management activities like fertilization and tilling that release excess nitrogen into the soil. This leads to N2O being produced upon microbial interaction.
To minimize climate change humanity must make concerted efforts across social, economic, and political institutions to reduce these emissions drastically and transition away from our dependence on fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind power, or low-carbon hydrogen fuels. Replacing technologies that use polluting fossil fuels with smart solutions that promote zero-waste living could be an effective approach to decreasing atmospheric contamination while simultaneously reducing heating due to CO2 accumulation. We can take responsibility for how we impact the environment and begin to mitigate it. Preservation measures such as reforestation help preserve biodiversity while also absorbing large amounts of harmful CO2 back into the natural world. This is a powerful way to address climate change and restore balance for future generations.
What are the causes of climate change?
Climate change is a worldwide phenomenon caused by an increase of human-generated greenhouse gasses emitted into the atmosphere. This is mainly due to fossil fuel burning for power and transportation. These greenhouse gases trap more heat from the sun, which causes global warming.
Other factors contributing to climate change include population growth, land clearing and destruction of ecosystems, deforestation, energy consumption, and over-grazing. This reduces the amount of carbon sinks naturally found in the atmosphere that absorb CO2. Changes in solar radiation and other natural forces can also contribute to climate changes.
These human activities together result in Earth experiencing an overloading of its energy budget. This has caused an average global rise of 1° Celsius over pre-industrial time. Glaciers melt quicker than they form, and sea levels rise because oceans absorb most the heat energy. Other negative consequences include water scarcity, droughts and extreme weather events like flooding and hurricanes.
It is vital that we reduce our carbon footprint immediately and stop releasing greenhouse gases. This will help us protect ourselves against further damage from climate change. Along with reducing our dependence upon fossil fuels to generate electricity, it is important to invest in renewable sources like wind turbines or solar cells that do not emit harmful pollutants into nature. These delicate planetary cycles are also susceptible to other sustainable practices, like reforestation.
What does climate change politics have to do with global efforts to combat it?
Climate change is a highly politicized issue that has created a great deal of division among nations, governments, and individuals. Politics of different actors can have an impact on the implementation of climate change measures. It has become increasingly difficult to come to an agreement on how to address this urgent environmental crisis globally.
A majority of scientists agree that climate change caused by humans is real and must be addressed immediately. These politics often hamper global cooperation needed to achieve effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices.
In particular, various governments around the world are keen to protect their economic interests and enforce measures that would limit business activities as little as possible; this frequently conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend for addressing climate change in an efficient manner. Without strong international commitments and wide-spread international action, it can be very difficult for any individual state or group of nations to address climate change effectively through legislation.
It is difficult to reach a consensus about how to address climate change because of differences in power dynamics between countries. Countries with more economic power may appoint themselves to be represented on international bodies for negotiations about the environment. This can lead the to divisive discussions between the countries' interests and the collective interest. Additionally, the potential side effects of implementing radical changes like geoengineering are being heavily debated at both national as well international levels.
In the same way, grassroots movements are fighting powerful opponents at the grassroots level. These include corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbyists looking to retain politically favorable positions.
Properly distributing resources allocated towards any intervention program while being mindful of political divisions between nations will be critical if any coordinated effort aimed at mitigating our current environmental crisis is going successfully to come to fruition.
What are the impacts of climate change on developing countries and communities?
Developing countries and communities are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change due to limited access to resources, healthcare systems, and technology. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause decreased crop yields. This will have a significant impact on poorer communities suffering from food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
Climate change will have long-term effects on resources, poverty, and health. This includes an increase in the number of vector-borne disease such as dengue fever or malaria. There will also be an increased risk of flooding from rising sea levels, combined with extreme weather events. This puts lives at risk in coastal locations where many people lack the necessary infrastructure and emergency services to evacuate. Building resilience against these risks necessarily involves mitigating greenhouse gas emissions but may require other measures such as improved management of freshwater resources and better access to health facilities which assists with prevention strategies for diseases like malaria.
How does human activity affect climate change
Climate change is due in large part to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Changes (IPCC), more than 70% global warming has been caused by humans since the middle of the 20th century.
Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels like oil, coal, and gas. This adds to already existing levels of atmospheric CO2, which act as a "greenhouse gas" by trapping heat from the sun in Earth's atmosphere and increasing temperatures even further. This leads to higher ocean levels as Arctic ice melts and scrambles weather patterns around the world leading to deadly storms, droughts, and floods which could affect food production and endanger human health.
Deforestation: Deforestation knocks out trees which sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks when they take it up during photosynthesis. Also, cutting down forests can increase albedo - which is the amount reflected solar radiation going back into space. It also reduces solar heat absorbtion by the earth's surfaces and encourages excessive global warming. As well decreases local air quality with deforestation being linked permanently with respiratory issues.
Farming: Each year, between 14% and 18% global anthropogenic greenhouse gases are released by the animal agriculture industry. Animal waste releases large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to its composition rich in methane bacteria Eating less or no animal products altogether can be an effective way to reduce your contribution towards global warming from this source alone., Agriculture itself also relies heavily on fertilizers which contain nitrous oxide released into our atmosphere directly harms humans creating smog from ground level ozone harming our respiratory system making polluted air hazardous for life.
Conclusion: Human activity has had a profound impact on the environment for centuries. However, technology has made it possible to leverage green innovation and make eco-friendly efforts to combat climate change. This will ensure that everyone is safe while prospering in nature.
What can be done to ensure a sustainable future, given the climate change challenges?
Sustainability is the ability for future generations to meet their current needs without compromising their ability to do the same. Climate change is presenting new challenges. We need to take immediate action to end our dependence on finite resources.
For a more sustainable future it is essential to rethink our current consumption and production models, as we also need to reduce our dependence upon natural resources such fossil fuels. We need to find new technologies, renewable energy sources, and systems that can reduce harmful emissions and still meet our daily needs.
In addition, it is essential that we adopt an integrated approach when looking at sustainability. This means that all aspects are considered, including the materials used, waste management strategies and reuse strategies, as well energy usage in transportation and industry. There are many potential solutions available including the utilization renewable energies like sun, wind, and water power; improved waste management systems; higher efficiency in agriculture; improved transport network; green building regulations; sustainable urban planning initiatives.
This goal requires behavioral changes from individuals in all sectors of society. Education programs are essential to assist people in understanding the impacts of climate change. They can also help them understand how they can contribute positively to a more sustainable planet through micro-actions like reducing food waste and adopting low-carbon lifestyles.
Only through cooperation between citizens, business leaders, and governments will we ever be able make substantial progress towards creating a sustainable world for future generations.
What's the current climate in the world? And how does it change?
The current climate situation is one of uncertainty and unprecedented change. Unprecedented levels in atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing global temperatures to rise significantly. This can lead to droughts and heat waves as well changing rainfall patterns, melting Polar ice caps, ocean acidification and rising sea levels.
These changes are already having a profound impact on ecosystems around the world, causing extinctions and disruption of habitats. They also threaten the livelihoods and lives of billions, especially in areas that are already suffering from resource scarcity and poverty.
Human activity has led to an increase in extreme weather events such as hurricanes, cyclones, floods, wildfires, etc. This trend will continue as temperatures continue rising.
A rapidly changing climate has many effects. They can impact everything from food insecurity to displacement by extreme weather events to sea level rise, causing communities to relocate. Climate change is also creating social inequalities bydisproportionately affecting marginalized populations that don't have the knowledge and resources necessary to adapt.
While some countries have made progress in reducing carbon emissions, or implementing renewable energy initiatives, global action has not been taken at the level necessary to combat these changes. All nations must unite to prevent further destruction and devastation by climate change.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy to Support a Low-Carbon Transition
Clean energy is any form of renewable energy that doesn't produce or emit pollution. It can include technologies such as solar photovoltaics, wind power and hydroelectricity. Clean energy sources offer many environmental benefits. These include a reduction in dependence on fossil fuels, reduced air pollution from traditional electricity methods, and more reliable access to remote areas.
By buying shares in companies involved in developing clean energy technologies, investors can get involved in these projects. This could be done by investing in publically traded stock, mutual funds, or ETFs related to renewable energies. To fund research and development in clean energy technologies, investors can also make direct investments in venture capital or start-ups.
Investors in clean energy support innovation that reduces the harmful effects of traditional sources of electricity generation. This investment may lead to economic growth by creating jobs related the production of renewable energies that require skilled labor. Lastly, investors may see a return on their investment in clean energy through tax incentives programs. These incentives encourage green technology investments such as solar panels, wind farms, and biomass heat production systems.
By investing in companies focused on creating cleaner sources of electricity from renewable resources such as sun, wind, and water while avoiding activities that could harm the environment, we can support the transition to a low-carbon future while reaping economic rewards at the same time.