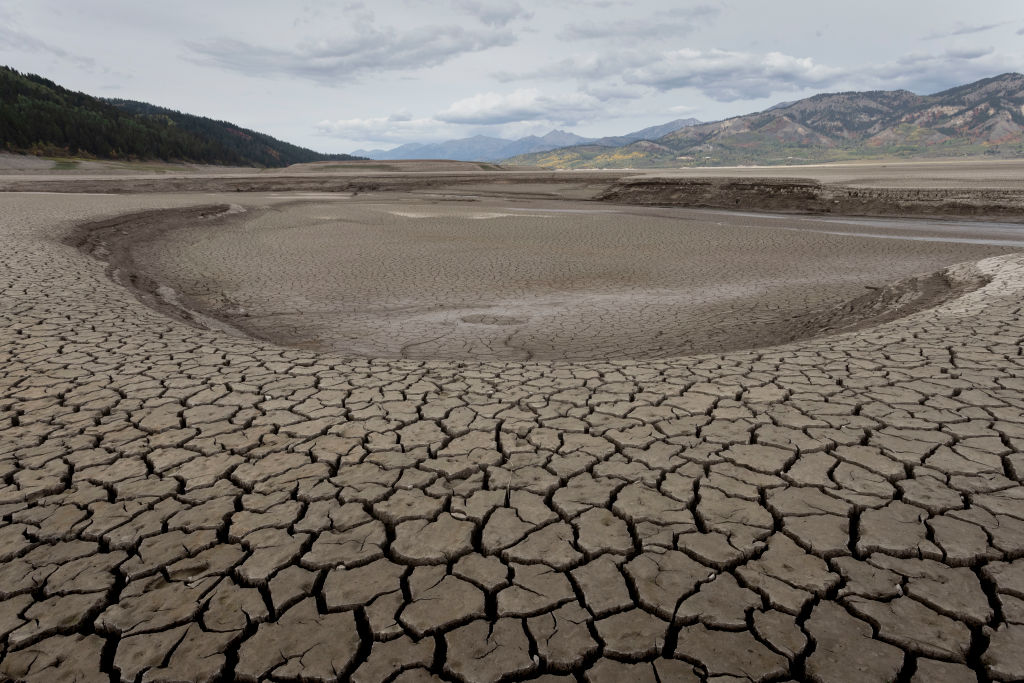

The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, (IPCC), released a new report detailing the consequences of climate change on Earth. It determined that the world must reduce its anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions significantly by 2030 if global temperatures are to remain below 1.5 degree Celsius (C). This would avoid severe consequences.
Five major risks are identified by the report. These are heat and drought, coastal flooding as well storm surges and sea-level rise. The "burning embers" chart, below, shows the severity of the risks at various levels of warming. Darker colors indicate greater stress levels.
Not only are there physical effects, but also socioeconomic ones. As an example, people may be more likely to be evacuated due to the increased likelihood of tropical cyclone and flood surges. This will increase the death toll from extreme weather events. According to the report, the number of people at risk from coastal climate hazards will increase to one billion by 2050.
The report acknowledges that many of the climate change impacts are already happening, but the magnitude of these impacts is far greater than was previously believed. Many species have had to shift their ranges. About half of land animals and plants moved to more favorable areas for survival.
Climate change has not only altered the ecosystems but also made it difficult to access food and water. As a result, millions of people are suffering acute food insecurity. The increasing heat and storminess is also affecting the availability water resources. Similarly, more than eight million people are currently displaced worldwide by natural disasters.
Over eight percent of terrestrial species are at high risk of extinction. This number is expected to increase to 13 percent by three degrees Celsius and to 15 percent by four degrees. There is also a greater risk of regional extinctions.
Increasing sea levels could make flooding more severe and lead to cities running out of water. The oceans are also warming, which can lead to hypoxia. This will make marine microbes less able to absorb oxygen. Further, more greenhouse gases will be released into the atmosphere by the melting Arctic permafrost.
The risk of drought is another threat to agriculture. Agriculture drought at two degrees is expected to be 150 to 2000% more likely. A decrease of 5 to 10% is expected in the yields of agricultural crops. Depending on the amount of CO2 that is released into atmosphere, zinc and other vital nutrients could be affected.
Other effects of climate change include changes to the amount of iron and zinc as well as protein and other nutrients. A study found that zinc will be reduced by 7 percent if there is an equivalent increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide. The same goes for protein. A CO2 equivalent increase will reduce it by 4%.
These findings are based on climate data from five global climate models. They are compared against two emission scenarios: one that is low and one that is high. Each one outlines different ways to reach macro-level conditions by 2030.
FAQ
How is extreme weather related to climate change
Global warming is directly responsible for extreme weather events such as heat waves and floods, droughts. Cyclones, storms and hurricanes are all a result of global warming. Global warming has caused an increase in atmospheric temperatures. This has had an impact on different weather phenomena worldwide.
According to climate scientists, the frequency of extreme weather-related catastrophes has more than doubled in the past 20 years. As sea temperatures rise, so do wind patterns. This can affect the distribution of hurricanes and storms in different geographic regions around the globe.
2015 El Nino brought warm water towards South America. This led to increasing temperatures at an alarming pace and heavy rains that caused floods and displacement in Peru, Bolivia and other countries. Many places, including Antarctica, have experienced their highest temperatures ever. This indicates a direct relationship between global warming trends as well as the frequency or occurrence of extreme weather events all over the globe.
Another example is Hurricane Irma which took place in 2017 causing $50 billion of economic loss not just to the USA's Florida but also to other states such as Puerto Rico, Cuba, etc proving once again that climate change is responsible for a dramatic increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, (IPCC), concluded that human activities are increasing severity of climate change. This naturally leads, in turn, to more severe and intense natural disasters globally. Thus, there is strong evidence concerning humans' relationship to extreme weather events occurring around us all.
What are the effects of climate change on the environment and society?
Climate Change has wide-ranging effects on the environment as well society. Climate change will have many impacts on the environment. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate disruption is already having profound impacts on the environment and society around the world. Global temperatures are expected to continue to rise and this will only get worse in the future.
Ocean levels rising due to melting ice caps is one of the most pervasive effects of climate change worldwide. This can lead to shoreline erosion and increased flood risk for coastal communities. In many countries, saltwater intrusion can also occur, affecting freshwater supplies in the coastal areas.
Extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts regularly occur across many countries around the world as a result of climate change. These events result in mass destruction of homes or businesses and can lead to relocation or complete loss of life. Extreme storms can also cause flooding and landslides, which increase the damage to infrastructure like roads and railways.
Wildfires caused by climate change also increasingly occur more frequently than they did before with devastating results both for habitats and people living nearby who may find their lives at risk due to poor air quality when these fires spread smoke across affected areas.
This drastic change in living conditions is often a result of displacement or even refugee situations. When people decide to leave their homes, either involuntarily or voluntarily, it can be because their town has become too dangerous or not habitable due the changed climate conditions.
People with respiratory diseases such as asthma are particularly vulnerable to dust storms from increased aridity. Furthermore, pest infestations are predicted to rise in tandem with warmer temperatures. This phenomenon is known as the 'greenhousebug'. Global food insecurity will continue to grow as fewer crops have lower nutritional qualities. This could potentially lead to more hardships for people already struggling to make ends work.
What are some of the solutions proposed to climate change? How effective are they?
Climate change has become one of the most urgent issues of our time. It requires government, businesses and citizens to pay attention. The signs of a disturbed climate system include rising temperatures, extreme weather and sea level rises, as well as melting polarice. Multiple solutions have been proposed to address this phenomenon. These solutions range from technological solutions to behavioral changes to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions: An array of solutions have arisen to address climate change through changes in technology. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power provide reliable, clean energy that has minimal environmental side effects. Electric cars using renewable energy are a great alternative to petrol vehicles. They can reduce urban air pollution significantly. Other technological solutions include reforestation projects that aim to increase carbon sequestration in trees and soil as well as coastal protection systems to protect vulnerable places against rising ocean levels.
Behavioral changes: Small adjustments to existing routines can make big differences in reducing emissions. This will help limit future climate disruption. For example, purchasing locally produced goods with shorter supply chains reduces emissions associated with transport costs for food. The use of public or active transportation, as well as reducing cost and air polluting simultaneously, is a good option. In the same way, better insulation in your home can help reduce dependence on gas boilers that heat your homes.
Geo-engineering: Geo-engineering involves large-scale interventions in natural systems deemed too risky due to potentially unforeseen consequences -- including widespread crop failure or depletion in fish populations - though thought to be worth researching nonetheless due to its potential efficacy at dealing with the problem more quickly than behavior alone may allow for human activity would need to rapidly balance current CO2 levels via some possible mechanisms such as using Sulfates aerosol injection into Earth's stratosphere - blocking sunlight before it reaches the Earth's surface - brightening clouds above them so they reflect more light back into space or removing Carbon dioxide directly out of the atmosphere through bioenergy capture storage systems coupled with Carbon Capture Storage (BECCPS).
The effectiveness and efficiency of these solutions will depend on how many producers invest in green alternatives. However, incentives such as electric Cars play an integral part in incentivizing alternative solutions. Other than increasing consumer awareness about their utility over time, it is possible to mandate alternative solutions via policies measures. This requires regulatory bodies that are willing to engage players further. Although nontechnological approaches can work at one level; solving the global warming problem requires all parties.
What are the impacts of climate change and global warming on agriculture and food security
Global warming and climate change are having a direct effect on food security and agriculture. The changing climate can impact rainfall patterns and temperatures as well as soil moisture levels. Extreme weather is also possible. This can disrupt farming activities, reduce crop yields and lead to losses of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can cause crop diseases and pests to multiply. It can also affect the ranges that are suitable for agricultural production. This can result in higher costs for food production, and worsening hunger and nutrition around the world.
Rising sea levels pose a further threat. They could inundate valuable agricultural land in many coastal areas, leading to higher salinity levels in wetlands, where important crops are grown. Changes in climate also have an impact on livestock production. In summer, high temperatures can lower fertility rates in animals like sheep and cattle. This can result in lower milk yields, which can worsen food insecurity.
Although the relationship between climate change, global warming, and other factors is complex, there are efforts being made by governments to mitigate them through adaptation strategies. These include strategic investments in climate smart agriculture (CSA), which allows governments around the globe to make strategic investments in adapting their agricultural systems. This involves promoting sustainable methods such as crop rotation techniques or genetic diversity through the conservation of native seed varieties, which help protect against negative impacts from extreme weather conditions or other environmental stressors caused by the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. Improvements must be made within existing infrastructure set-ups so that necessary actions may be taken when critical crop thresholds are hit - this includes introducing stable irrigation networks with adequate access water supplies at times of the year when there is reduced availability due to warmer climates or intense downpours washing away much-needed access water resources outside planting seasons. Effective collaboration is key to creating lasting solutions that allow for the continual adherence to international dietary guidelines concerning quality nutrition in changing climates around the world. This includes all levels of government, NGOs and local communities.
What are the ways climate change can be mitigated or reduced?
There are many steps that can be taken in order to reduce and mitigate climate change's effects. These include reducing greenhouse gases emissions by using better energy practices and other sources of electricity, improving land management, protecting forests and wild places, protecting against extreme weather, investing in sustainable transport, strengthening early warning system for disasters, starting a research programme on the impact climate change has on biodiversity and ecosystems. Also investing in green technologies like solar cells or wind turbines, encouraging sustainable consume habits, and implementing environmental regulations across all segments of society. It is important to increase public awareness about climate change as it makes people feel accountable for their actions.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
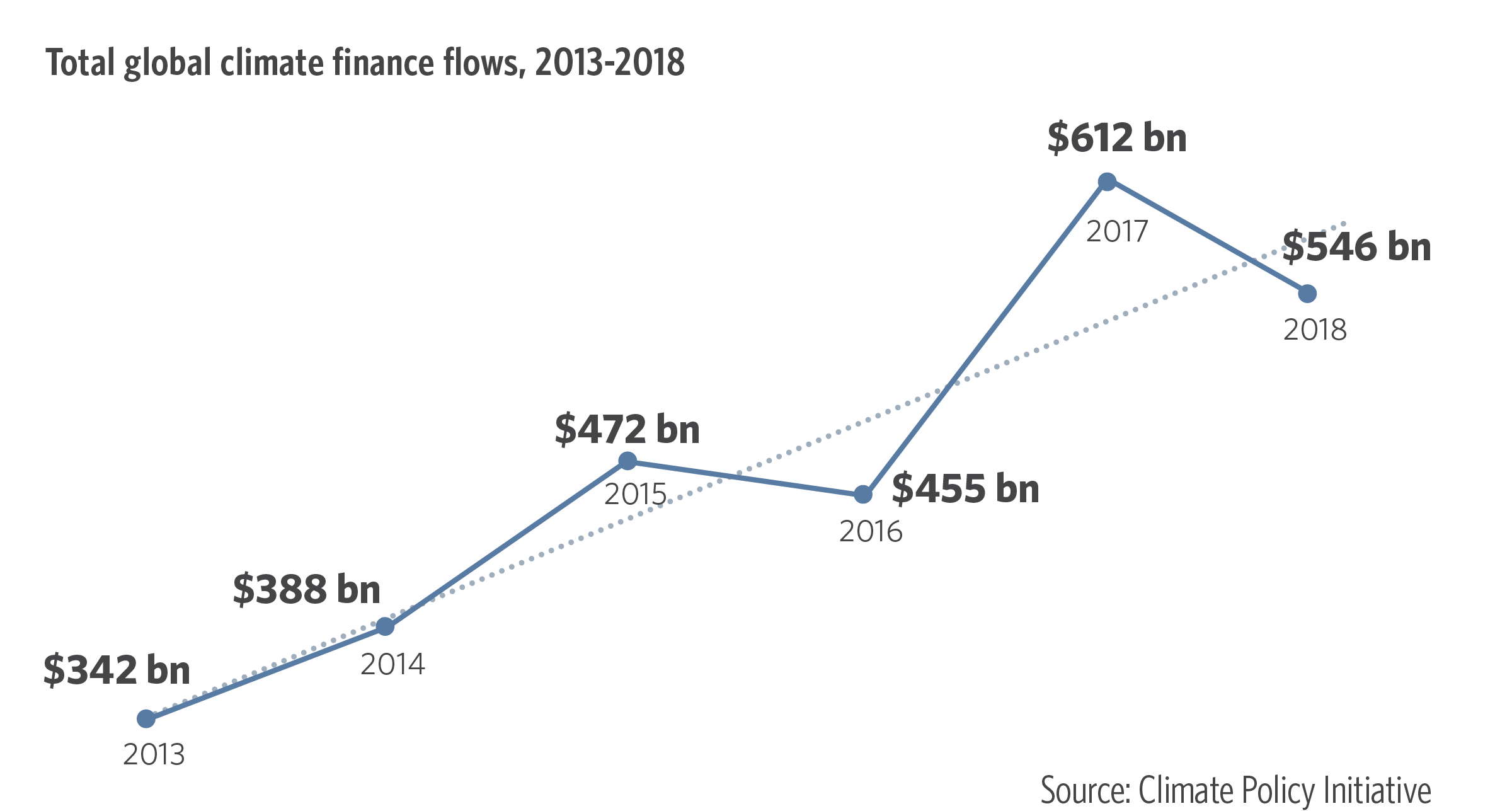
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy to Support a Low-Carbon Transition
Clean energy is any form of renewable energy that doesn't produce or emit pollution. It encompasses technologies like solar photovoltaics and wind power. Investing in clean energy sources can have many environmental benefits, such as reducing reliance on fossil fuels, reducing the amount of air pollution generated by traditional electricity methods, and providing more reliable electrical access to remote locations.
By buying shares in companies involved in developing clean energy technologies, investors can get involved in these projects. This could include investing in mutual funds, stocks that are publicly traded, or ETFs (exchange-traded fund) that deal with renewable energy. Investors may also be interested in direct investments in start ups or venture capital projects that fund research and technology development.
Clean energy investors are supporting innovation that helps to reduce harmful emissions from conventional sources of electricity generation. This investment could lead to greater economic development as it may create jobs in the field of producing renewable energy systems, which require engineers and skilled labor. Finally, putting money into clean energy can provide investors with a financial return due to tax incentives programs that are incentivizing investments into green technologies like wind farms, solar panels, and biomass heat generation systems.
By investing in companies focused on creating cleaner sources of electricity from renewable resources such as sun, wind, and water while avoiding activities that could harm the environment, we can support the transition to a low-carbon future while reaping economic rewards at the same time.